渲染函数
Vue3对render函数的使用做了简化,主要在于props的扁平化,可以看看下面的例子:
js
// Vue2 API
render(h) {
return h('div', {
attrs: {
id: 'box'
},
on: {
click: () => console.log('click')
}
}, 'hello vue2')
}js
// Vue3 API
import { h } from 'vue'
render() {
return h('div', {
id: 'box',
onClick: () => console.log('click')
}, 'hello vue3')
}- 在Vue3中,
h函数可以直接通过import来引入;在Vue2中,当我们分割渲染函数时,需要不断传递该h变量,在Vue3可以避免这个麻烦的操作了。 - 按照惯例,所有以
on开头的属性,都会被自动绑定为一个监听器; - 另外,也不需要考虑属性是应该绑定在
attrs还是props,Vue3会先检查属性是否在原生DOM中属于属性key,如果属于,就会自动设置为原生属性,反之,作为props传递给组件。
链接
- Vue3 Template Explorer:可以看到我们的模板被编译成什么样子
练习
接下来我们配合插槽的使用来完成一个练习。
在Vue3的中,插槽被保存在$slots对象中,默认是$slots.default,如果需要具名插槽,则使用$slots.xxx来获取。
题目:
html
<!-- 将下面这个组件模板,渲染成嵌套分级树列表 -->
<Stack>
<div>hello</div>
<Stack size="4">
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
<Stack size="4">
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
</Stack>
</Stack>
</Stack>
<!-- 得到下面这个结构 -->
<div class="stack">
<div>
<div>hello</div>
<div class="stack">
<div class="mt-4">
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
<div class="stack">
<div class="mt-4">
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>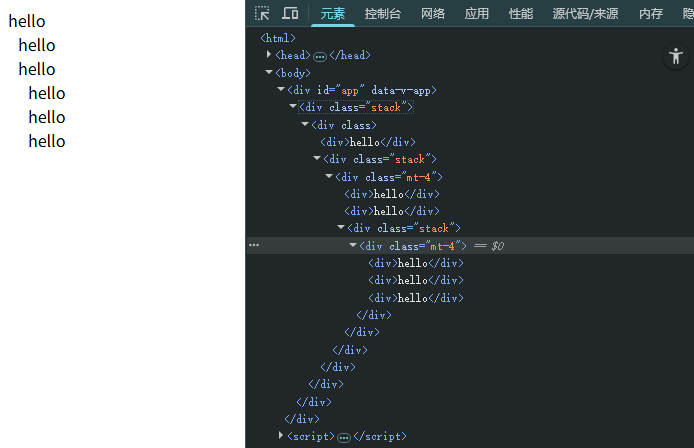
将下面的代码补充完整:
html
<script src="http://unpkg.com/vue@latest"></script>
<style>
.mt-4 {
margin-left: 10px;
}
</style>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const { h, createApp } = Vue
const Stack = {
// TODO
}
const App = {
components: { Stack },
template: `
<Stack size="4">
<div>hello</div>
<Stack size="4">
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
<Stack size="4">
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
<div>hello</div>
</Stack>
</Stack>
</Stack>
`
}
createApp(App).mount('#app')
</script>答案:
js
// 省略其他代码
const Stack = {
props: ['size'],
render() {
const slot = this.$slots.default
? this.$slots.default()
: []
return h('div',{ class: 'stack' }, h('div', {
class: [
this.$props.size ? 'mt-' + this.$props.size : ''
]
}, slot))
}
}